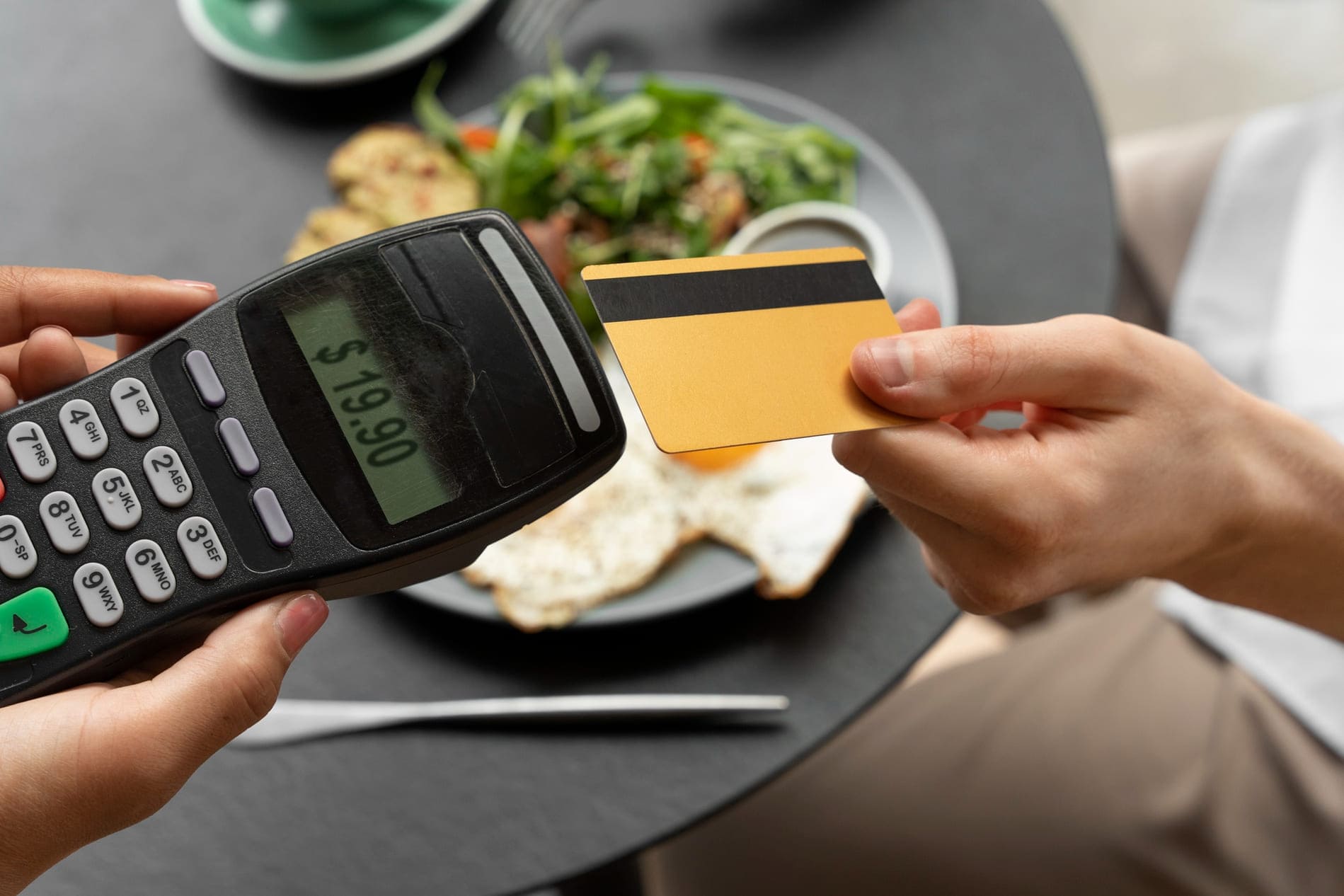
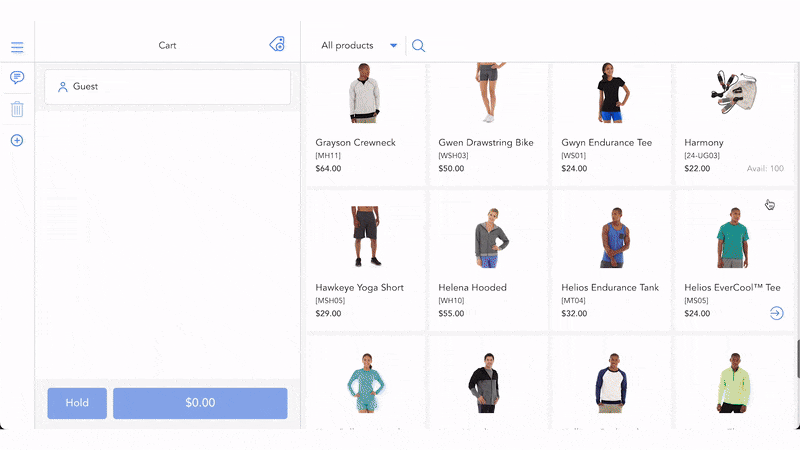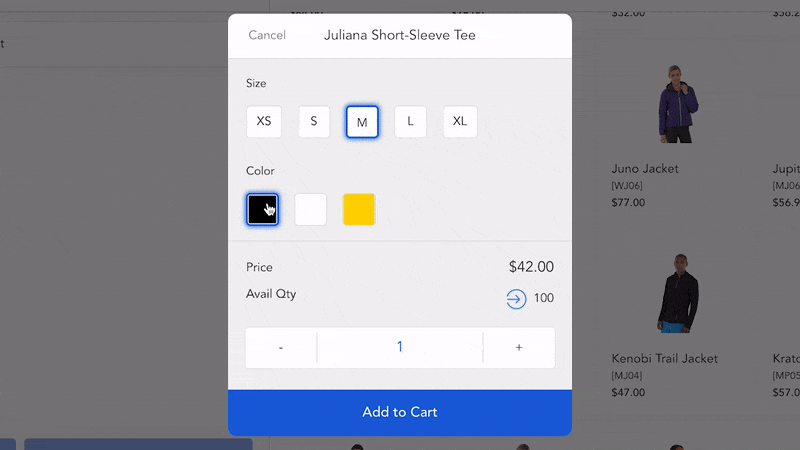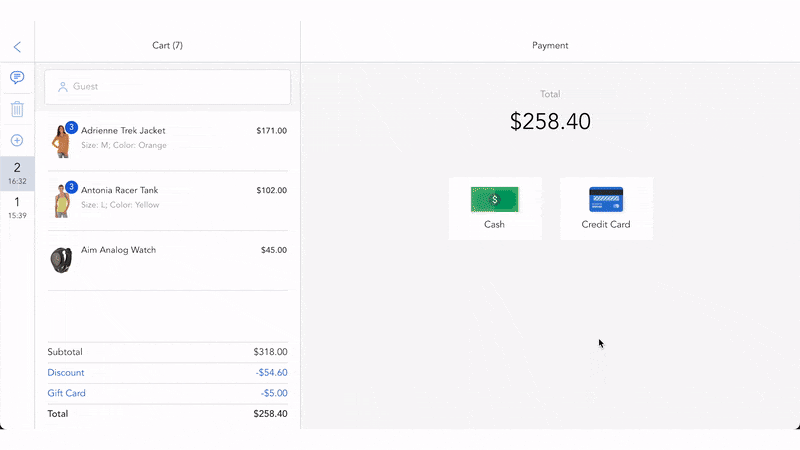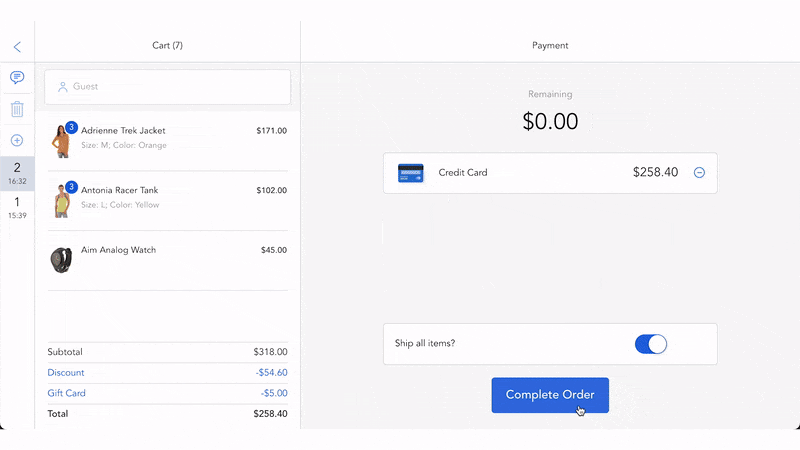
Cash and paper checks are giving their way to electronic payments – a fast, convenient, and easy payment method favored by massive numbers of shoppers worldwide. Recent statistics reveal the undeniable popularity of electronic payments. In 2023, credit cards, debit cards, and digital wallets, among other electronic payment types, accounted for up to 41%, 28%, and 15% respectively of the total in-store payments in the U.S.
The appeal of electronic payments primarily results from the convenience and speed they offer shoppers and the easier financial control they give businesses. Electronic payments accommodate the new payment demands of online shopping growth and international trade while diminishing the inherent limitations of traditional methods. As a result, retailers of any size should deploy electronic payments for their businesses to obtain enormous advantages.
To equip merchants with an essential understanding of electronic payments, this post illuminates some core aspects of this payment method. Read on to learn about what it is, how it works, how many types it has, and the way to optimize payment processing.
What is an electronic payment?
First, let’s clarify the electronic payment definition!

An electronic payment, or e-payment, is a payment method that allows customers to pay for goods and services employing electronic means and channels. Instead of cash or paper checks, shoppers use credit, debit cards, or digital wallets to pay for their point of sale or online purchases.
Customers can execute electronic payments at both online and physical stores. One of many electronic payment examples is when a consumer buys a piece of furniture at a Walmart store, they can wave their debit cards over an electronic payment machine to finalize the transactions.
Electronic payments often entail various technologies such as mobile wallets and electronic payment apps. Besides, security measures like encryption and tokenization help protect sensitive payment data from fraud or other potential hazards. At present, there are loads of reliable electronic payment platforms like Square, PayPal, and Stripe.
Electronic payment methods are advantageous to both retailers and shoppers. With these payment types, customers can enjoy faster, more secure, and seamless payment processing. Shoppers don’t have to waste time writing cheques or withdrawing cash from banks. They only need to perform a few simple steps to complete transactions. Additionally, electronic payments provide a wider array of payment options so customers can opt for the most suitable one. Customers can also make payments anywhere and anytime at their convenience.
On the business side, electronic payment solutions streamline payment processing for greater operational efficiency. More impressively, they aid transaction data tracking and financial management. Both businesses and customers can save plenty of time and costs associated with traditional payments like paper or postage.
4 types of electronic payment systems
Let’s compare the various electronic payment methods to see which one merchants should deploy for their business.

Credit and debit cards
Electronic payment cards are prevailing methods at physical stores. The number of transactions using credit and debit cards in the U.S. is estimated to reach 57% in 2027. Credit cards are a form of credit while debit cards directly deduct funds from customers’ current account balances. Despite different advantages, these types of electronic payment systems ensure customers great convenience and security.
To initiate an electronic card payment, customers have to manually enter payment details at the checkout page or provide a physical card at the point of sale. Merchants who accept card payments often need to pay processing fees per transaction.
ACH payments
ACH (Automated Clearing House) e-payment facilitates secure fund transfers between accounts at different banks or financial institutions through the ACH network. Typical types of ACH transfers include direct deposits and direct payments, which can cater to different payment scenarios such as tax refunds, employee payroll, and electronic bill payments. ACH transfers are somewhat slower than other electronic payment methods, but they often come with low or no costs.
Another form of payment that also operates via the ACH network is e-check. Electronic check payment, a digital version of paper checks, enables funds to be electronically moved from the payer’s checking account to the recipient’s account via ACH payment. This payment method is faster and safer than paper checks.
Digital wallets
These e-payment types make use of payment apps to store the customers’ payment information. Customers can download an electronic payment app on their smartphones or tablets and use these devices to directly pay for their purchases. Digital wallets also allow customers to tap their devices over POS terminals to make NFC contactless payments.
Mobile wallets eliminate the need for entering credit card information, thus accelerating the electronic payment process. This payment type also lets shoppers easily track their payment history. Besides holding card details, digital wallets can store other data like gift cards, coupons, and membership cards. The most popular apps on the market now are Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, each of which charges different fees for their services.
Internet banking payments
An Internet bank transfer or banking payment enables funds to be moved electronically from one account to another via any device connected to the Internet. Customers can check account balances, make electronic payment transfers, and manage their accounts instantly via a secure website or mobile banking app that the banks offer.
Internet banking payments are fast, easy, and safe. Customers must provide their usernames, passwords, and sometimes OTP codes to verify and carry out transactions. This electronic payment method also allows customers to make one-off or regular payments without visiting the bank.
How does electronic payment work?

There are different parties involved in processing electronic payments, including merchants, customers, electronic payment gateways, payment processors, customer banks (issuing banks), and merchant banks (acquiring banks). Businesses also need to have a merchant account to receive e-payments. The electronic payment systems normally work as follows.
- Customers enter essential payment details at the checkout page on your eCommerce site. Otherwise, customers can give payment information by dipping cards or waving mobile devices over a POS terminal at physical stores.
- The online platform or the POS terminals send the received payment data to the electronic payment gateway, which encrypts and submits the data to the payment processor.
- The payment processor verifies and transmits the data to the acquiring bank, which then delivers the information to the card network. The card network communicates with the issuing banks to ask for authorization.
- The issuing bank decides whether to reject or approve the transactions after checking the validation, authenticity, and available funds of the customer’s account.
- The electronic payment processor transfers the denial or approval for the transaction back to the payment gateway, which informs the merchant and customer whether the transactions are successful.
- After that, the customer bank moves the funds to the merchant bank within a set period.
- The merchant bank sends the payment to the retailer’s accounts with some fees deducted.
Pros and cons of electronic payments

Advantages of electronic payments
- Enhance customers’ convenience: Electronic payments are fast and convenient, letting customers swiftly pay for their purchases within minutes. They come in diverse forms and types, so customers can pick their favorite electronic payment options. By accelerating transaction processing, these payment methods shorten customers’ waiting times at the checkout, minimizing frustrations and potential lost sales. Consequently, you can strengthen customer loyalty and get more repeat sales.
- Improve business efficiency: With electronic payments, businesses process orders faster with fewer errors, thus optimizing their overall operations. Besides, merchants who facilitate electronic payments via POS systems that integrate with accounting tools have their transaction data automatically recorded. Hence, businesses can reduce errors caused by manual data entry while still closely tracking and managing their financial data.
- Reduce costs: Electronic payments minimize the costs often associated with traditional methods, including expenses on paper, postage, and even manual labor. Cross-border transactions also cost less when utilizing electronic payments than traditional ones.
- Ensure security: Electronic payments offer stricter security than paper checks or cash. Major electronic payment processing services implement advanced security technologies, including encryption and authentication methods, into their solutions to safeguard payment details and payment processes from fraud.
Disadvantages of electronic payments
- Technical issues: Electronic payments heavily depend on technologies, which otherwise brings some downsides. Unexpected issues such as power outages, Internet loss, system downtimes, or technical software errors might halt the transaction processing.
To mitigate these problems, make sure you choose a reliable and robust online electronic payment system to avoid frequent bugs. Besides, also examine the support that the service provider offers to ensure you get timely help when problems arise. - Security risks: Although electronic payments guarantee a higher level of security than traditional methods, they’re still under considerable cyber threats. As customers have to reveal their card details or bank account information, they might be vulnerable to identity theft, electronic payment fraud, unauthorized use, or phishing scams.
To reduce the risks of fraud and data breaches, merchants should choose an electronic payment system that employs the latest security protocols and comply with industry security standards like PCI DSS. - Transaction fees: Another critical disadvantage of electronic payments is that merchants have to pay fees for each successful transaction. The particular amounts rely on the payment methods and the service provider. Therefore, retailers should carefully research the cost structures of some electronic billing and payment solutions before making final decisions.
Optimize payment process and control electronic payments in retail
An appropriate electronic payment solution is decisive in elevating customer experience and improving business efficiency. To see which one best fits your business, you should consider several factors as follows.
- Payment options: Check whether your chosen services support the payment methods that your customers prefer.
- Fee structures: Analyze the fee structures of your favorite payment providers to see what types of costs you have to pay.
- Compatibility: Make sure your go-to electronic payment software connects well with your existing POS system, accounting tools, and other business applications.
- Security: Secure your payment process by choosing the services that utilize advanced security technologies and ensure compliance with popular security standards.
- Customer support: Go for a payment solution that provides timely support to any arising issues.
Besides a trustworthy payment service provider, multi-channel and multi-location retailers also need a robust POS system to enable effective electronic payment management. Magestore supplies retailers with powerful and intuitive Magento POS and POS for Shopify to assist in processing payments and simplifying business operations.
Magestore POS is compatible with multiple electronic payment facilitators such as Stripe and Square electronic payment services to process numerous payment types. Moreover, Magestore POS software integrates smoothly with diverse business tools such as accounting software and ERP to sync key business metrics in real time. On that basis, you can get a holistic and accurate view of your current business situation to make necessary changes.
>>> Explore more: Full-featured omnichannel Stripe Point of Sale
Conclusion
Electronic payments use technologies to speed up transaction processing while shielding payment data from fraudsters. On the one hand, customers can pay for their purchases with credit cards, debit cards, or any other electronic payment method they find convenient. On the other hand, businesses can streamline their business operations, enhance customer experience, and get more sales. Undoubtedly, these payment methods are becoming the norm for both online and cross-channel retailers.
To choose the best fit among many electronic payment services, remember to consider key factors like security, available payment options, and cost structures. Also be aware of the downsides of these payment types, so you can handle them properly.
FAQs
1. What is electronic check payment?
Payment by electronic check, or e-check, is a form of payment that utilizes digital checks rather than conventional paper checks. The e-check payments allow moving funds from the payer’s account to the payee’s account electronically via the Internet or other networks.
2. What are digital vs electronic payments?
Electronic payments refer to any payment made without cash or paper checks. Meanwhile, digital payments are an electronic payment type made from a digital device like a computer or a smartphone. Digital payments don’t involve using physical credit or debit cards.
3. What are the differences between electronic payment vs wire transfer?
Electronic payments consist of many payment types such as credit cards, ACH transfers, and mobile wallets. However, wire transfers fall under the electronic payment umbrella, which transfers funds from one bank account to another using messaging networks such as SWIFT or Fedwire.
4. How to make an electronic payment?
You can make an electronic payment with physical credit or debit cards, digital wallets, or ACH transfers.
5. Are electronic payment systems safe?
Yes, electronic payment processing solutions are normally safe. These systems often employ security technologies such as encryption, tokenization, and authentication methods to ensure safety and security.
6. Can I use electronic payment for checkout when there is no internet connection?
You can check out using electronic payment when there is no internet connection thanks to the POS offline mode. However, it is up to the electronic payment platform that whether they support finalizing payment in offline mode or not. It is better that you check with your provider for this information.