Are you finding the solution to optimize your backorder management? Or simply, researching new ideas to apply for your business. Backorder might be an ideal solution for many retailers to boost sales volumes and revenues during season holidays. However, it only works if you’re doing right for your business.
In this article, we will unlock the secret of backorder accumulated during our practical implementation experiences with global retailers from multiple industries. Let’s see how backorder works and how to minimize backorder effectively.
What does backorder mean?

Backorder is a business order yet to be fulfilled because stock is unavailable.
It means that customers can order items that are out of stock in order time, so merchants don’t miss the deals. Merchants need to be transparent when the items are available and try to fulfill them within the timeframe.
For example, when your customer shop on your online website, they can place an online order with out-of-stock items and get a message that they will get their order shipped when items are replenished. In many cases, if the item is restocked soon, merchants can ship the order to customers without using the backorder feature.
In many business retail cases, backorder is an important part of the fulfillment process and requires a professional system to ensure orders are fulfilled in time to customers.
The difference between backorder and preorder
Store owners should distinguish between backorder and preorder. Some people still misunderstand these terms because both of them allow a customer to order and pay for items that are NOT currently in stock.
However, they have some differences in purpose. For preorder, retailers allow customers to order although items are not released yet.
By launching a preorder program, store owners can forecast sales and get early money going to the business. Retailers can know exactly which items consumers want and how much they have to prepare to fulfill the demand.
Opening a preorder campaign also creates a room to satisfy the psychological need of being first. Some people are proud of being the first people that can afford the latest items so they’re willing to wait.
However, in the backorders, items were launched and sold already. For example, on Black Friday, sales quickly go to the peak, some items in store are sold out within one hour after opening the door. Retailers offer customers to create a sales order with items that are out of stock and delivered later.
That makes sense because merchants don’t want to lose customers.
Let’s dive into more details about why store owners need to offer backorders in the following paragraph.
Why should merchants have backorder?

Minimize customer dissatisfaction
Here’re some cases that commonly occur in retail.
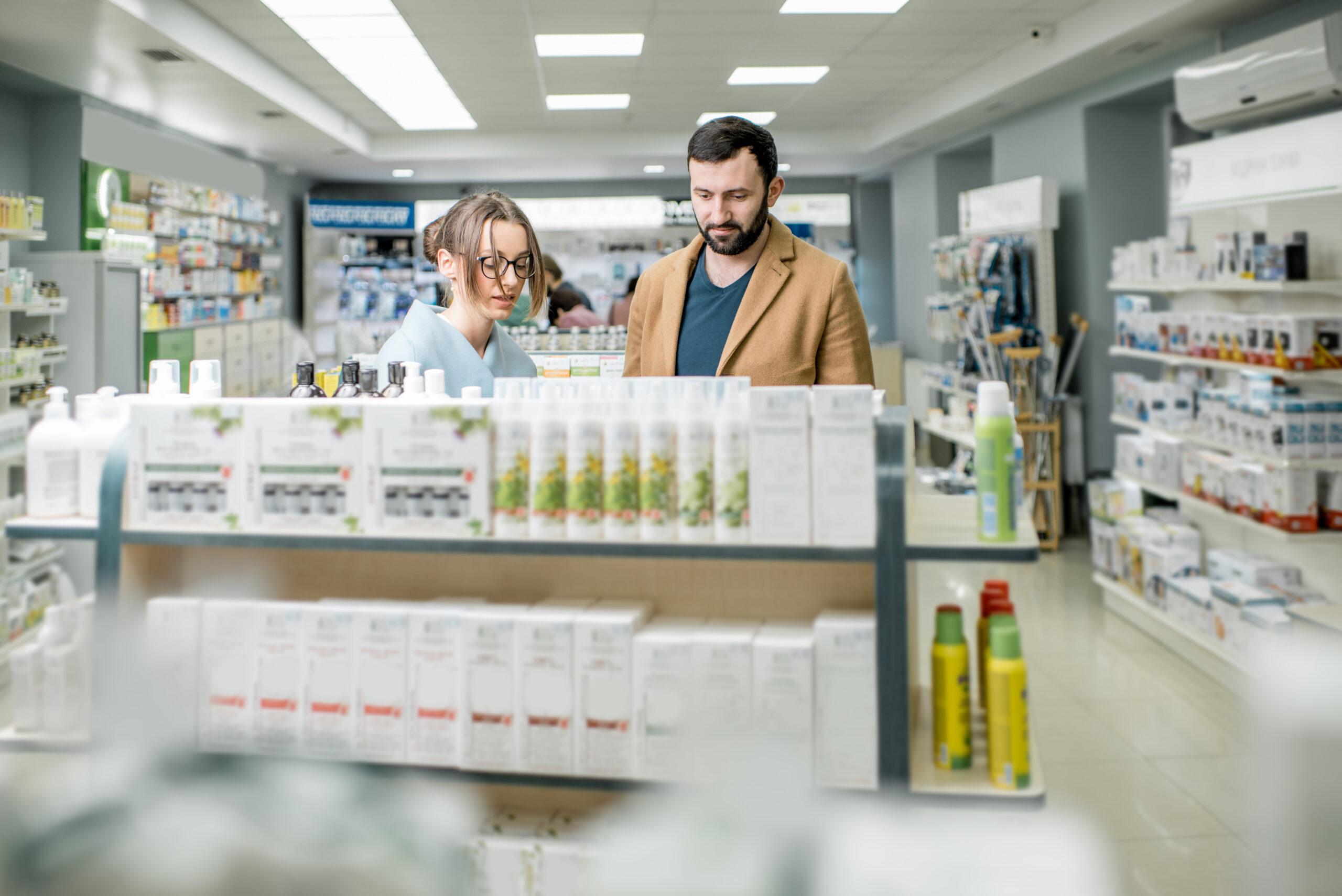
Case 1: A customer browses and searches your jean jacket catalog on your website. After that, she decides to order 3 jackets for her and her friends. However, only 2 items are available.
Case 2: A customer is interested in a T-shirt promoted on social media. Then, he goes to your offline store to buy it. However, staff detects that the item has been sold out some minutes ago.
What should you do in these situations? Simply say that you’re out of product and let customers leave with disappointment? It can hurt consumers. They’ll go to other stores and never come back.
However, if you know that items will restock quickly, offering a backorder is one way to show your efforts to fulfill. It partly reduces customer disappointment.
Cut inventory costs
Managing inventory is always a challenge for retailers. It’s not only about the cost you spend to import items from suppliers, but also other costs. It can be caring cost, holding cost, maintenance, or operational controls.
According to conveyco.com, as of June 2019, U.S. retailers are sitting on approximately $1.36 of inventory for every $1 in sales.
By allowing backorders, merchants don’t need to hold too many items in the warehouse. Thanks to this, they can save related inventory costs.
Backorder process and best practices
Process of backorder
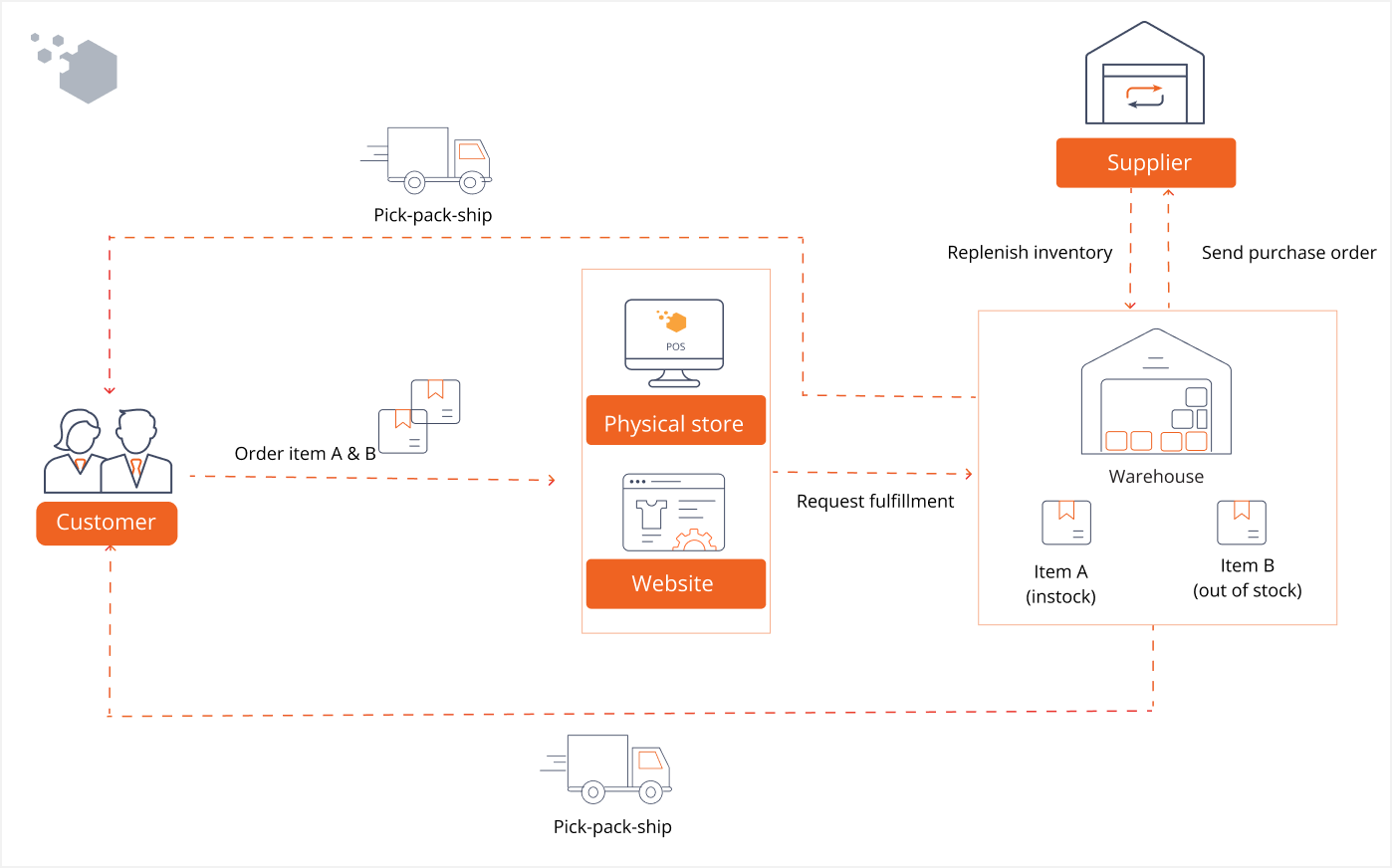
To implement a backorder solution for your business, you need to get knowledge of how the customer journey and also the fulfillment process look.
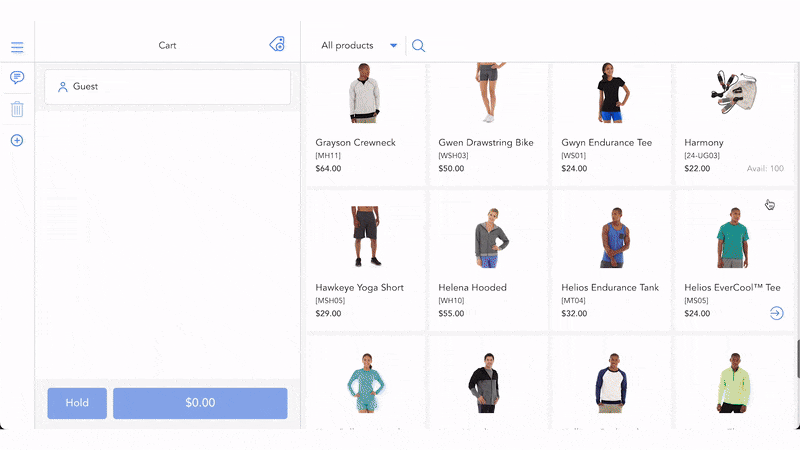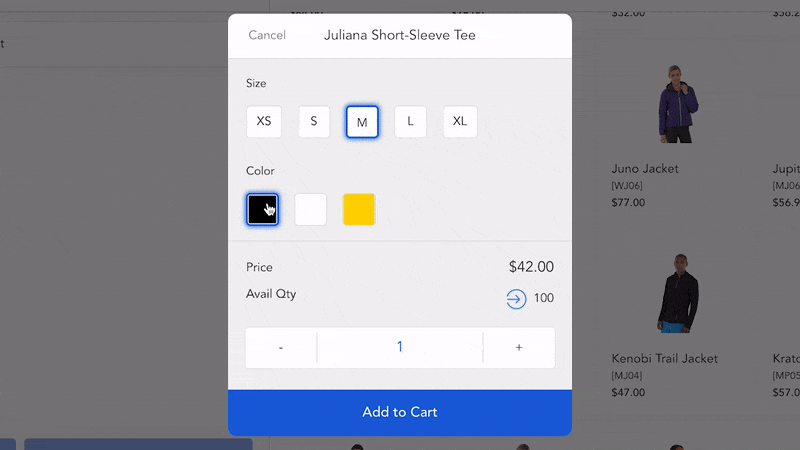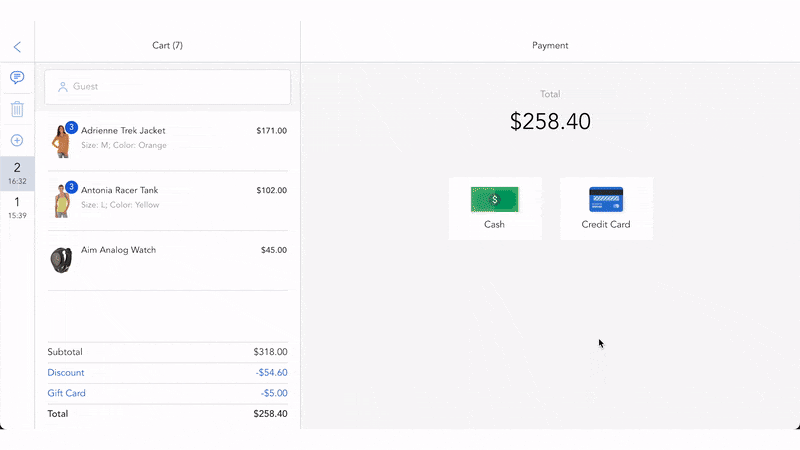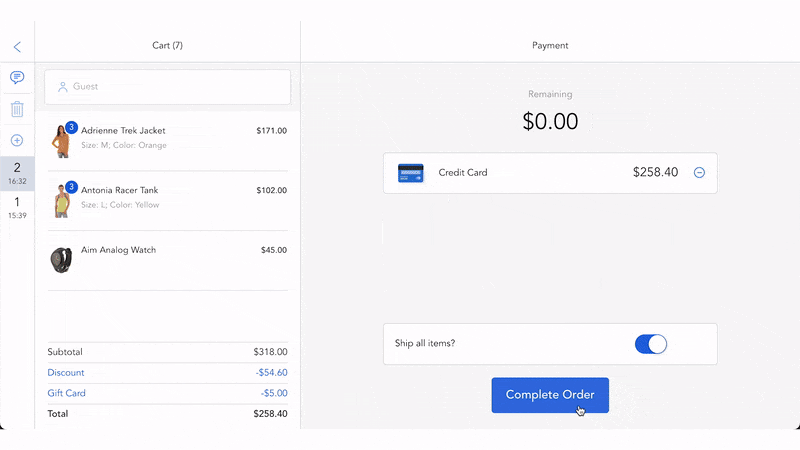
Step 1. Customers go to the website and add items to the cart. The system shows information that items are not available now and predicted time to deliver. If customers are willing to wait, they continue to create backorder.
In the case, customers shop in offline store, staff checks stock in POS system and informs customers about the sold-out. Then, asks the customer for a backorder.
In one purchasing transaction, not all items are out of stock. Depending on how the business manages orders, staff and the system will split into 2 orders or keep in only one order.
Step 2. Fulfillment staff will have to create purchase orders to restock items. Then, get approval for the purchase order if necessary. However, for some reason, an item you’ve ordered is taking longer than expected to arrive. It’s important to inform customers of the new estimated arrival date.
Step 3. Staff receives items sent by suppliers and storages them in the warehouse.
Step 4. Staff pick, pack, and ship items to customers. Besides, customers can also want to pick items in store.
Best practices
Implement a system that enables the backorder process
With backorder, you’ll be under the pressure of keeping your promise to fulfill within a time frame defined with customers. That’s why using a manual system or Excel files to manage the backorder process can be time-consuming.
To make everything faster, retailers should manage this process in a system. It’s better if you implement it in an ERP system that supports inventory and fulfillment.
Based on consultation experience for global retailers, we list down some essential features as follows.
System admin can set up whether a product is back-ordered or not in each sales channel. It’s because not all items are available to backorder. Also, one item can be back-ordered online but not in the offline store.
Then, customers can add out-of-stock items to shopping if they order on the website. In brick-and-mortar stores, the staff is likely to scan or add items on the POS screen to create orders.

The system should distinguish backorders from other orders by listing them on a separate session or marked with the label “Backorder”. Staff can create purchase orders from the list of backorders to restock quickly. Even if the items are mainly provided by one supplier, the system should create purchase orders automatically. Then, staff just need to verify and confirm purchase orders.
Besides, purchase orders should link to the original backorder so that staff can prepare for pick-pack-ship to the right sales order after they receive items.
Work closely with suppliers
When lead times are longer than expected, customers may not be patient to wait and then cancel orders. Thus, merchants lose sales and customer trust.
It could also result in a high stock level in the case the customer cancels orders during items coming from suppliers.
To avoid that, retailers should work closely with suppliers to get updated on back-ordered items. Based on this, they inform the correct delivery time.
Besides, a good relationship with suppliers can help merchants to collaborate on acquiring a faster delivery, allowing retailers to fulfill their customers sooner than a given time.
Final words
Backorder is quite common in the retail world now. It helps businesses improve customer experience while lowering inventory costs.
Backorder for Magento is an available feature in our Magento POS and Retail Store Software (RMS) that allows merchants to fulfill out-of-stock orders and manage PO with suppliers. If you’re a merchant looking to build a backorder solution for your business, feel free to contact our experts for a free consultation.